We use cookies to ensure that we give you the best experience on our website. If you continue to use this site we will assume that you are happy with it
Sealing Juvenile Records: What Happens When You Turn 18
 Written by Background Check Repair
Written by Background Check Repair
Criminal Records | June 17, 2024

Table of Contents
Sealing juvenile records can be an important decision for many people to make. What happens when you turn 18? Can an old arrest still cause problems for someone who is now an adult? There are a few things to consider when sealing juvenile records, but turning 18 doesn’t automatically mean that every issue will be solved immediately.
There are still instances where your juvenile record can be used against you in a court of law. If someone wants to buy a gun or join the military and they have unsealed criminal history as a juvenile, they would not be legally allowed to do so.1 It is also possible for an employer to look at your juvenile court record and use this information against you during an interview process. Understanding what information remains on your record is important because sealing juvenile records does not always ensure they cannot be accessed by third parties.
Do Sealed Records or Juvenile Records Show on Background Checks: The Laws Concerning Sealed Criminal Records
Many states will seal the records of a juvenile after that person has turned 18 years of age (be sure to understand the background check type this applies to). In these states, this is the case even if the individual has been convicted of a crime. By sealing these records, courts ensure that this information is kept private and away from public view.
Sealed juvenile records are typically restricted and can only be accessible by court order. However, it is crucial to understand that sealing these records does not mean they will completely disappear. In fact, there are still instances where your record may show up on a background check.
Although juvenile records may be sealed, the accompanying police reports, juvenile court proceedings, arrest records, and even witness statements can still show up on some background checks. It is also possible for information from juvenile records to appear in the public domain, such as when it is accessed during court cases or by government agencies.
While criminal records that are either completely sealed or expunged may not show up on a background check, the accompanying court documents can still be accessible.
The Fair Credit Reporting Act (FCRA) prohibits employers from discriminating against job applicants based on their criminal history. Title VII of the Civil Rights Act and the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission also prohibit discrimination based on the use of criminal history when it pertains to certain protected minority groups.2 However, it is still possible for a potential employer to evade these regulations by looking back further into an applicant’s past in order to find any additional information. This means sealing juvenile records may not protect you from being disqualified for employment if some court records or police reports are still obtainable and lawfully used in a hiring decision.
It is essential to understand how sealing juvenile records impacts the remainder of your criminal history, as it does not always guarantee that information will disappear or stay private. By sealing these records, however, your past may not negatively affect future employment opportunities if an employer only chooses to access public records during a background check.
Can You Seal a Record Without a Lawyer? What Forms Are Required for Sealing Criminal Records?
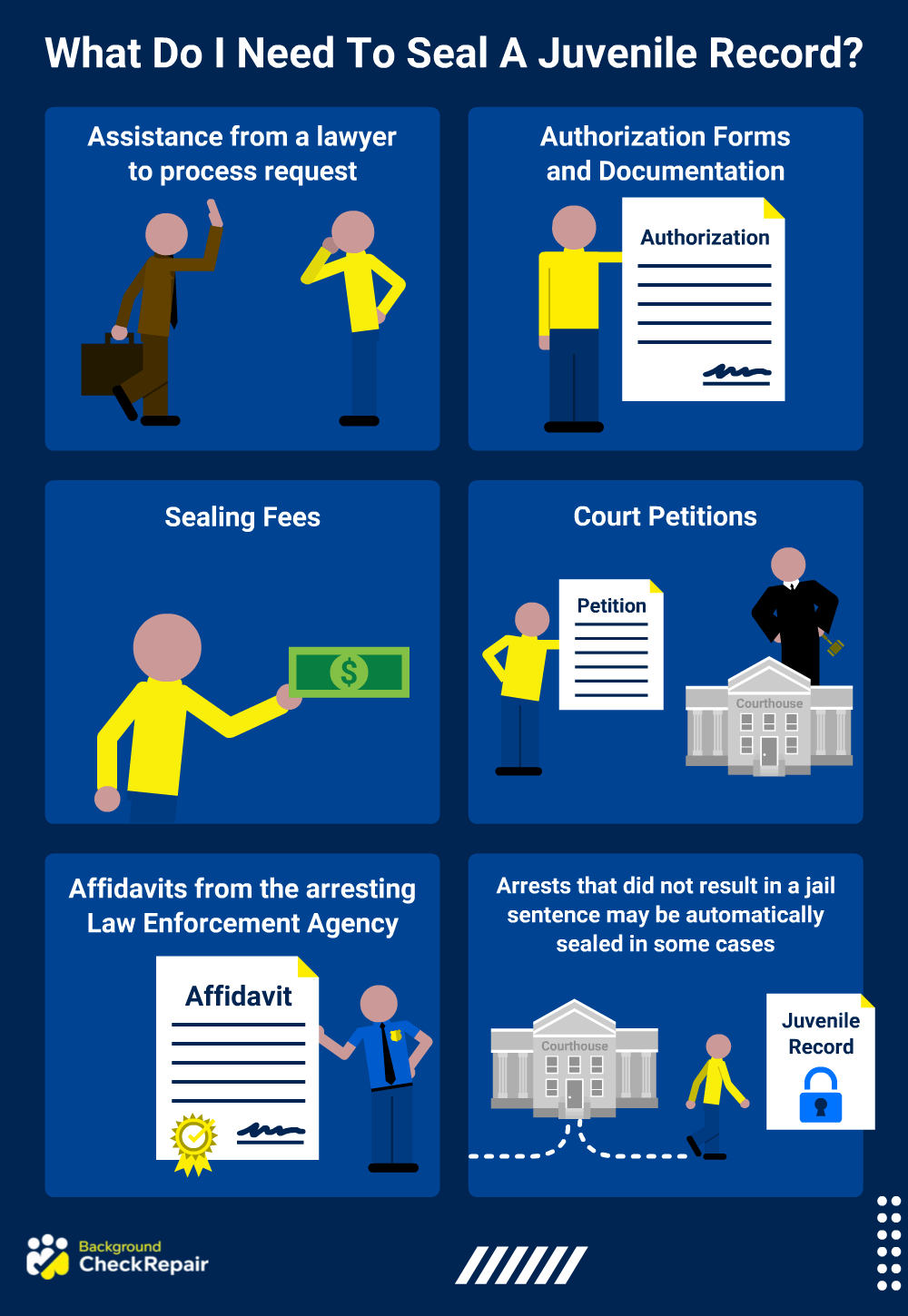
It is not always necessary to hire a lawyer to seal criminal records. In some cases, states will automatically seal certain records to prevent them from being found on a simple background check, such as those related to arrests and convictions that never resulted in a jail sentence or incidents involving juveniles.
When sealing and removing criminal records from background checks, it is imperative that you know which offenses require a lawyer to process the request so that you can legally avoid any penalties stemming from your past actions. Certain states will allow sealing without an attorney if all of the required sealing record forms are completed correctly, and sealing fees are paid.
In sealing juvenile records, you should make sure that you have all of the forms required by your state. For example, sealing a criminal record as a juvenile can involve court petitions as well as affidavits from the arresting law enforcement agency and state departments, if applicable.
Defense attorneys will ensure that the necessary steps are taken in order to seal these juvenile records for you. They will petition the courts on behalf of their clients, ensuring that all of the correct paperwork is filed correctly.

Sealing juvenile delinquency records can be a daunting task for those who have reached adulthood. However, sealed records may help to protect your past from being used against you when it comes to future employment opportunities or in obtaining certain types of government funding or licensing. Although sealing your juvenile history will not necessarily allow you to escape the past, it may help to keep these records out of public view.
It is important to note that sealing criminal records without a lawyer may not be advisable or effective. Understanding what steps need to take place for sealing criminal records can be complicated. Even if an individual has successfully sealed their record, they still may experience issues related to the information being accessible.
The forms and documentation required to seal a record can be found at your local clerk of court’s office. A petitioner who is seeking to seal criminal records will be required to sign a legal petition and, depending on your state’s rules, may need to file this motion in the court where the incident took place. Other forms that may be needed include authorization forms or paperwork showing proof of filing fees.
State laws related to sealing criminal records differ significantly, and various statutes and regulations must be followed. Sealing a record is never a guarantee that this information will remain separate from the public eye.
Furthermore, details in criminal records can vary greatly depending on where you live. Even if you successfully have your juvenile records sealed, it may still be possible for these charges and convictions to show up on background checks performed by law enforcement, government agencies, or private security firms who are granted special access.
To ensure that prior arrests and convictions as a juvenile are not reported to third parties, it is advisable to expunge juvenile records instead. Records sealing juvenile crimes or infractions are still available under certain circumstances, and as previously noted, sealing a record may not prevent the conviction from showing up on background checks. A juvenile court petition to expunge juvenile court records will be more effective, ensuring that your past mistakes do not haunt you after you have turned 18.
Sealing California Juvenile Records: State Laws Regarding Juvenile Records Sealed in CA
The state of California has its own laws regarding sealed juvenile records and what information is accessible to the public (especially when a free California background investigation is used which has different requirements for if you need permission to run the check). Like sealing criminal records, sealing juvenile records may not always be possible and will depend on your age and the type of crime that was committed.

According to California law, if a case is dismissed by the juvenile court, it may automatically be sealed.3 Individuals who were found not guilty can also request that their records be sealed, which can occur either at the court’s discretion or if a motion is filed.
In addition, sealing juvenile criminal records is possible for charges that have been reduced to an infraction. For less serious juvenile crimes, a record may be sealed as long as you were between the ages of 14 and 18 years old when the incident occurred. While sealing a record is possible after minor crimes, it will depend on your age and what charges were filed. Felonies and violent crimes are not eligible for sealing.
Sealing juvenile records can be complicated, but there are steps you can take to make sealing your record easier. Understanding the laws related to sealing criminal records and sealing California juvenile records is vital in ensuring that this process goes as smoothly as possible.
Sealing Juvenile Records and Expungement
While sealing a record may not always be possible depending on your personal circumstances, understanding what removing criminal records can entail will allow you to manage the process more efficiently. In most cases, in order to seal a conviction from a juvenile record, individuals will need to wait until they are 18 years old or older. In many states, those serving probation may be eligible to ask to have a record sealed if they successfully complete their sentence, without any additional violations.
Ensuring that juvenile records are sealed not only benefits those who were convicted of a misdemeanor crime from unfair repercussions, it can also provide more opportunities for them in the future. Criminal records can impact college, job, and housing opportunities for those who were convicted of a crime, even as a minor.
If you need to seal juvenile records or have ever asked yourself the question, “will I pass a background investigation with a misdemeanor,” consider contacting a lawyer who can guide you through the appropriate request process. If you prefer to expunge records, understand that this will require petitioning the court. Expunging juvenile records will remove these records from your criminal history while sealing juvenile criminal records will keep them separate but available to law enforcement and other government agencies. Expungement may be a better option to pursue if sealing juvenile court records is not automatically available to you.
If a juvenile is convicted of a misdemeanor crime before turning 18 years old, the sealing process could allow the conviction to be removed from their record. This can help someone avoid unfair repercussions as an adult. If you are concerned sealing these juvenile documents will still allow them to appear on background checks, expunging juvenile court records may be more appropriate for your situation. Understanding how to get a background check report on yourself by using a reputable screening agency can help you make the right decision when choosing between these two options.
The process for expungement will require petitioning the court with certain documentation, though there are many benefits associated with doing so, including removing any references to crimes committed. It is important to understand that the sealing process will not remove these records from your criminal history, records from juvenile court can still be accessible or made available by court order.
Once you have completed certain eligibility requirements or waited until you are old enough to petition for sealing or expungement, it is important to understand your rights. Sealing juvenile records and expungement can both be beneficial and provide more opportunities for those who were convicted while under age.
References
1Rose, Veronica. 8 March 2006. JUVENILE FELONY RECORD AND GUN PURCHASES. OLR. 29 November 2021. Web. <https://www.cga.ct.gov/2006/rpt/2006-r-0212.htm#:>
2U.S. Equal Employment Opportunity Commission. 25 April 2021. Enforcement Guidance on the Consideration of Arrest and Conviction Records in Employment Decisions under Title VII of the Civil Rights Act. 29 November 2021. Web. <https://www.eeoc.gov/laws/guidance/enforcement-guidance-consideration-arrest-and-conviction-records-employment-decisions>
3Judicial Council of California. 2021. Sealing Juvenile Records. 29 November 2021. Web. <https://www.courts.ca.gov/28120.htm?rdeLocaleAttr=en>
